Redefine the planets!
Only a proposal not the current definition,
Started 2024-05-07

Only a proposal not the current definition,
Started 2024-05-07
This site aims to redefine the categorization of objects in our solar system and beyond, aligning these definitions more closely with what the average person perceives. While I don't claim to know what everyone thinks, these are my thoughts, and I hope others may agree

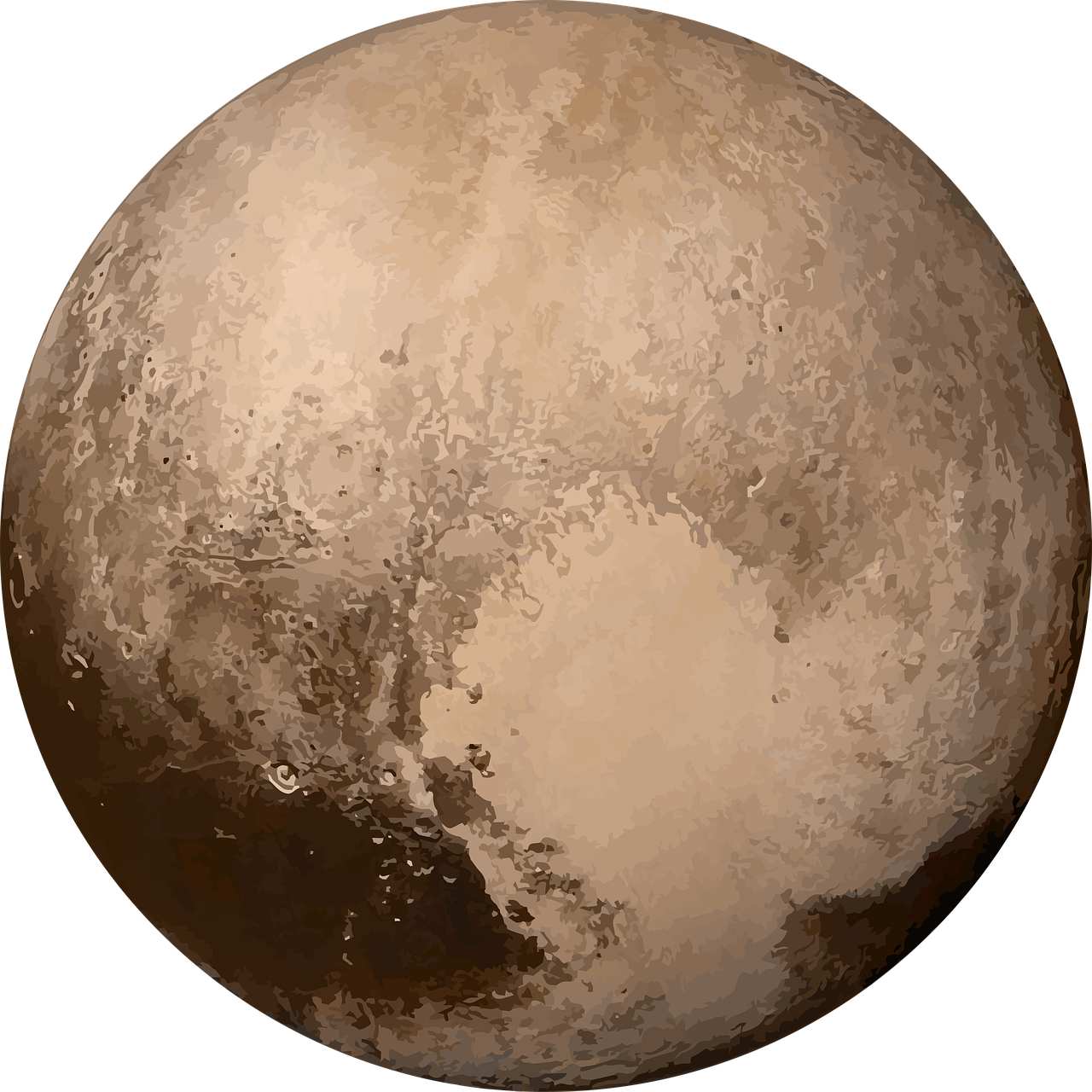
Today's planetary definitions, I believe, need revisiting to make them more comprehensible to the layperson. These definitions should better reflect the common understanding of celestial bodies, without compromising the scientific rigor needed to define parameters like diameter, mass, or hydrostatic equilibrium. For instance, the current definition excludes Pluto, which many of us grew up recognizing as a planet. However, my motivation isn't nostalgia; it's about simplification and accessibility.
Take, for example, the moons of Saturn and Jupiter. The term "moon" seems to apply to just about any small rock orbiting these planets. In my view, a "moon" should be a rounded object in orbit, not just a small rock with a diameter of 1000 meters.
At the time of writing, Saturn has 145 moons, and scientists are likely to discover more. It's unreasonable to expect the average person to keep track of all these moons, let alone our solar system's current count of 8 planets and their moons. Why not simplify the definitions for non-professionals and hobbyists?
These definitions aim to be straightforward yet robust. While scientists will still be needed to determine the specific criteria that differentiate one type of object from another, the broad outlines could?and should?be accessible to everyone. Below, you'll find my proposed new definitions. This definition would result in a total of 10 planets, 48 moons and a lot of moonoids and pebbles.
The term 'apparent' is used here to acknowledge that some celestial bodies may have additional layers of different states of matter that are not immediately visible. For example, Earth has an atmosphere, but its apparent surface is solid. Jupiter, on the other hand, likely has a solid core, but its apparent surface is gaseous.

